
Maintaining accurate records of depreciation and amortization isn’t just a best practice; it’s an absolute necessity for businesses. Accurate record-keeping ensures compliance assets = liabilities + equity with tax laws and accounting standards, and it also provides the data you need to make informed financial and managerial decisions. Understanding the impact of depreciation and amortization on your financial statements and business valuation cannot be overstated.
- In accounting, the treatment of amortization expense is a critical aspect of accurately representing a company’s financial position and performance.
- Backed by 2,700+ successful finance transformations and a robust partner ecosystem, HighRadius delivers rapid ROI and seamless ERP and R2R integration—powering the future of intelligent finance.
- For the Depreciation method, the straight-line method can be used as well.
- In this post, you are going to find the differences between depreciation and amortization in detail.
- But the accounting standards are different for depreciation and amortization.
Analysis of Depreciation of Tangible Assets
- A loan doesn’t deteriorate in value or become worn down through use as physical assets do.
- Analysts and investors in the energy sector should be aware of this expense and how it relates to cash flow and capital expenditure.
- Amortization and depreciation aren’t just accounting rules; they’re tax strategy and planning tools.
- Both allow businesses to deduct the cost of an asset over its useful life, which can reduce taxable income and, as a result, decrease the amount of tax owed.
- The difference is depreciated evenly over the years of its expected life.
- They impact financial reporting by lowering the reported value of assets on the balance sheet and reducing net income on the income statement.
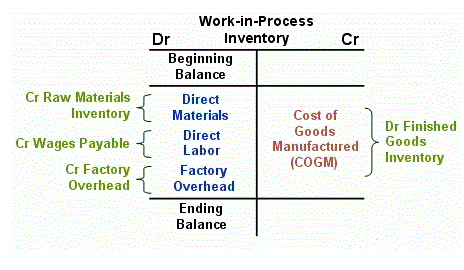
Because both depreciation and amortization are using the straight-line method, the two items can be combined into a single figure in the filing. For example, an asset costing $21,000 with a $1,000 salvage value and a useful life of ten years would depreciate at $2,000 per year under the straight-line method. Here, the business expenses the same percentage of the asset’s value each year. Because the percentage is applied to a constantly shrinking number, the dollar value of the expense becomes smaller with each passing year. The amortization formula is a simple calculation of dividing the cost of the asset by its useful life in years. To calculate straight-line depreciation, the company needs to know the cost of the asset, its useful life, and its salvage value, if any.
Keeping Accurate Records: A Necessity for Businesses
In the early stages of an amortizing loan, a larger portion of the payment goes toward interest. Later in the loan term, more of the principal is paid off with each payment. Thomson Reuters provides expert guidance on amortization and other cost recovery issues that accountants need to better serve clients and help them make more tax-efficient decisions. These types of depreciation are mandated by law and enforced by professional accounting practices all over the world.
Balance
The choice of method depends on the nature of the intangible asset, the pattern in which the asset’s economic benefits are expected to be consumed, and the accounting policies of the company. However, if the benefit from the asset decreases over time, or if it’s linked to production levels, alternative methods like the declining balance or units of production might be more appropriate. Both amortization and depreciation are non-cash expenses that reduce the value of assets over time.

How to Report Depreciation and Amortization for Tax Purposes
It uses Depreciation Rate decided as per accounting standards and is applied on physical assets. Under the general rules, intangible assets are paid off, tangible assets are devalued. As a result, balance depreciation can be estimated using the straight line method, amortization vs depreciation while tax depreciation is based on one of the accelerated methods. Throughout the period of fixed assets use, the value shown in the balance gradually decreases. The possibility of spreading some costs over a period of several years is one of the most important accounting concepts.
- The practice of spreading an intangible asset’s cost over the asset’s useful lifecycle is called amortization.
- With amortization, even though there are six acceptable calculation methods to choose from, the cost is usually spread evenly over the useful life of the asset.
- Now that we know what intangible and tangible assets are, let’s talk more about how amortization and depreciation are used to account for each.
- During the next fiscal year, depreciation charges are once again housed in the account.
- Its value depends on factors like popularity, image, prestige, honesty, fairness, etc.
- These are governed by specific tax laws, which often allow for accelerated depreciation or different amortization schedules.
- In addition, there is a difference in the methods of calculating balance and tax depreciation.
Depreciation accounting software
The depletion deduction enables an individual to account for the product reserves reduction. There is no set length of time am intangible asset can amortize it could be for a few years to 30 years. The depreciation class includes an asset account which appears as an asset in the balance sheet, and therefore it maintains a positive balance. This depreciation class is under assets subject to depreciation, and it shows in the balance sheet as the net depreciable asset together with the depreciation sum account. Depreciation is a measured conversion of the cost of an asset into an operational expense. Depreciation affects the net income reported and balance sheet of a company.
Straight-line method
The methods for depreciation are also meant for amortization if the latter is evaluated for loans and advances. In that case, the above methods of amortization schedule of loans are used. The properties, including buildings, equipment, tools, machinery, etc. let businesses manufacture and produce goods that they sell to generate revenue. Any damage to these ultimately affects the value of those properties, causing depreciation. For example, in a damaged plant resale, buyers would hardly take interest in buying it unless the sale value is low. In a world where financial accuracy is paramount, your records are a testament to your business’s financial integrity and reliability.

A company purchases an industrial printer for Outsource Invoicing making professional brochures and pamphlets. Explore why HR often manages payroll, when finance steps in, and how companies balance compliance, efficiency, and employee needs. Fraud poses a significant threat to small businesses, often due to limited resources and oversight mechanisms. In 2024, consumers reported losing over $12.5 billion to fraud, a 25% increase from… Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers.
What is the Difference Between Amortization and Depreciation?
If an organization wants to change the method of depreciation, then the retrospective effect is to be given. Any surplus or deficit arising on account of such change in the method of depreciation shall be debited or credited to the profit & loss account as the case may be. A Fixed Asset is a long-term asset (or non-current asset), one that a business will hold for longer than a year. These are permanent, tangible items the business intends to own long-term (more than a year). These Fixed Assets may be referred to as Property, Plant, and Equipment assets or PP&E. If you pay the principal amount of $2,000 yearly, the amortized loan should be $2,000.
In other words, the depreciated amount expensed in each year is a tax deduction for the company until the useful life of the asset has expired. Over time, these processes reduce the value of a company’s equity, changing the financial statement’s appearance and impacting the analysis of the company’s performance and financial health. In the world of accounting and finance, the terms “depreciation” and “amortization” are frequently encountered.
